 京公网安备 11010802034615号
经营许可证编号:京B2-20210330
京公网安备 11010802034615号
经营许可证编号:京B2-20210330
scikit-learn的线性回归模型
特征选择的方法
作为有监督学习,分类问题是预测类别结果,而回归问题是预测一个连续的结果。
|
|
TV | Radio | Newspaper | Sales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 230.1 | 37.8 | 69.2 | 22.1 |
| 2 | 44.5 | 39.3 | 45.1 | 10.4 |
| 3 | 17.2 | 45.9 | 69.3 | 9.3 |
| 4 | 151.5 | 41.3 | 58.5 | 18.5 |
| 5 | 180.8 | 10.8 | 58.4 | 12.9 |
|
|
TV | Radio | Newspaper | Sales |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 196 | 38.2 | 3.7 | 13.8 | 7.6 |
| 197 | 94.2 | 4.9 | 8.1 | 9.7 |
| 198 | 177.0 | 9.3 | 6.4 | 12.8 |
| 199 | 283.6 | 42.0 | 66.2 | 25.5 |
| 200 | 232.1 | 8.6 | 8.7 | 13.4 |
特征:
TV:对于一个给定市场中单一产品,用于电视上的广告费用(以千为单位)
Radio:在广播媒体上投资的广告费用
Newspaper:用于报纸媒体的广告费用
响应:
Sales:对应产品的销量
在这个案例中,我们通过不同的广告投入,预测产品销量。因为响应变量是一个连续的值,所以这个问题是一个回归问题。数据集一共有200个观测值,每一组观测对应一个市场的情况。
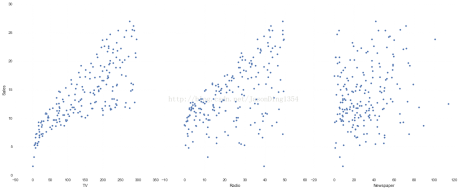
线性模型表达式: y=β0+β1x1+β2x2+...+βnxn 其中
y是响应
β0是截距
β1是x1的系数,以此类推
在这个案例中: y=β0+β1∗TV+β2∗Radio+...+βn∗Newspaper
|
|
TV | Radio | Newspaper |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 230.1 | 37.8 | 69.2 |
| 2 | 44.5 | 39.3 | 45.1 |
| 3 | 17.2 | 45.9 | 69.3 |
| 4 | 151.5 | 41.3 | 58.5 |
| 5 | 180.8 | 10.8 | 58.4 |
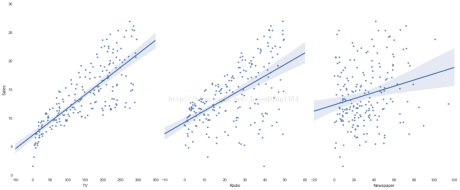
y=2.88+0.0466∗TV+0.179∗Radio+0.00345∗Newspaper
如何解释各个特征对应的系数的意义?
对于给定了Radio和Newspaper的广告投入,如果在TV广告上每多投入1个单位,对应销量将增加0.0466个单位
更明确一点,加入其它两个媒体投入固定,在TV广告上没增加1000美元(因为单位是1000美元),销量将增加46.6(因为单位是1000)
下面介绍三种常用的针对回归问题的评价测度
(1)平均绝对误差(Mean Absolute Error, MAE)
1n∑ni=1|yi−yi^|
(2)均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE)
1n∑ni=1(yi−yi^)2
(3)均方根误差(Root Mean Squared Error, RMSE)
1n∑ni=1(yi−yi^)2−−−−−−−−−−−−−√

数据分析咨询请扫描二维码
若不方便扫码,搜微信号:CDAshujufenxi
在金融行业的数字化转型进程中,SQL作为数据处理与分析的核心工具,贯穿于零售银行、证券交易、保险理赔、支付结算等全业务链条 ...
2025-12-24在数据分析领域,假设检验是验证“数据差异是否显著”的核心工具,而独立样本t检验与卡方检验则是其中最常用的两种方法。很多初 ...
2025-12-24在企业数字化转型的深水区,数据已成为核心生产要素,而“让数据可用、好用”则是挖掘数据价值的前提。对CDA(Certified Data An ...
2025-12-24数据分析师认证考试全面升级后,除了考试场次和报名时间,小伙伴们最关心的就是报名费了,报 ...
2025-12-23CDA中国官网是全国统一的数据分析师认证报名网站,由认证考试委员会与持证人会员、企业会员以及行业知名第三方机构共同合作,致 ...
2025-12-23在Power BI数据可视化分析中,矩阵是多维度数据汇总的核心工具,而“动态计算平均值”则是矩阵分析的高频需求——无论是按类别计 ...
2025-12-23在SQL数据分析场景中,“日期转期间”是高频核心需求——无论是按日、周、月、季度还是年度统计数据,都需要将原始的日期/时间字 ...
2025-12-23在数据驱动决策的浪潮中,CDA(Certified Data Analyst)数据分析师的核心价值,早已超越“整理数据、输出报表”的基础层面,转 ...
2025-12-23在使用Excel数据透视表进行数据分析时,我们常需要在透视表旁添加备注列,用于标注数据背景、异常说明、业务解读等关键信息。但 ...
2025-12-22在MySQL数据库的性能优化体系中,索引是提升查询效率的“核心武器”——一个合理的索引能将百万级数据的查询耗时从秒级压缩至毫 ...
2025-12-22在数据量爆炸式增长的数字化时代,企业数据呈现“来源杂、格式多、价值不均”的特点,不少CDA(Certified Data Analyst)数据分 ...
2025-12-22在企业数据化运营体系中,同比、环比分析是洞察业务趋势、评估运营效果的核心手段。同比(与上年同期对比)可消除季节性波动影响 ...
2025-12-19在数字化时代,用户已成为企业竞争的核心资产,而“理解用户”则是激活这一资产的关键。用户行为分析系统(User Behavior Analys ...
2025-12-19在数字化转型的深水区,企业对数据价值的挖掘不再局限于零散的分析项目,而是转向“体系化运营”——数据治理体系作为保障数据全 ...
2025-12-19在数据科学的工具箱中,析因分析(Factor Analysis, FA)、聚类分析(Clustering Analysis)与主成分分析(Principal Component ...
2025-12-18自2017年《Attention Is All You Need》一文问世以来,Transformer模型凭借自注意力机制的强大建模能力,在NLP、CV、语音等领域 ...
2025-12-18在CDA(Certified Data Analyst)数据分析师的时间序列分析工作中,常面临这样的困惑:某电商平台月度销售额增长20%,但增长是来 ...
2025-12-18在机器学习实践中,“超小数据集”(通常指样本量从几十到几百,远小于模型参数规模)是绕不开的场景——医疗领域的罕见病数据、 ...
2025-12-17数据仓库作为企业决策分析的“数据中枢”,其价值完全依赖于数据质量——若输入的是缺失、重复、不一致的“脏数据”,后续的建模 ...
2025-12-17在CDA(Certified Data Analyst)数据分析师的日常工作中,“随时间变化的数据”无处不在——零售企业的每日销售额、互联网平台 ...
2025-12-17